Celtis occidentalis (sel’-tis ok’si-den-tae’-lis)
Family: Ulmaceae, Elm
Key Steps
- 1b – Alternate leaf arrangement — go to 18
- 18a – Leaf simple — go to 19
- 19b – Thornless — go to 22
- 22e – All leaves unlobed — go to 31
- 31d – Leaf is oval or oblong (twice as long as wide) — go to 41
- 40a – Leaf base asymmetrical — go to 41
- 31d – Leaf is oval or oblong (twice as long as wide) — go to 41
- 22e – All leaves unlobed — go to 31
- 19b – Thornless — go to 22
- 18a – Leaf simple — go to 19
Description
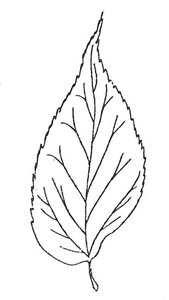 Leaf: Medium to light green, uneven base, widest at base, 3-7 inches long. Coarsely toothed except smooth at base. Net-like venation, 3 conspicuous veins branching from base. Long narrow tapering tip. Hackberry Nipple Gall (small round balls) usually found on underside of leaf.
Leaf: Medium to light green, uneven base, widest at base, 3-7 inches long. Coarsely toothed except smooth at base. Net-like venation, 3 conspicuous veins branching from base. Long narrow tapering tip. Hackberry Nipple Gall (small round balls) usually found on underside of leaf.
Bud: Usually arranged in two rows along the stem. Buds are very small, narrow, pointed, pressed close to stem. Hard to see. Scales are hairy.
Leaf Scar: Crescent-shaped, raised. Three bundle scars. Stipule scars.
Stem: Slender, grayish, zig-zaggy. Lots of gray lenticels on young growth.
Bark: Gray-brown to dark brown. Older bark is “warty” or knobby.
Pith: Usually chambered throughout or near leaf scars; white, small.
Flower: Female is greenish, solitary, in leaf axil. Male in clusters of 1, 2 or 3, at base of new growth.
Fruit: Solitary, edible, round berries hang down from branches. Start out orange-red and turn to dark purple.
Habit: Irregular branching, large shade tree, vase-shaped, dense, broad, spreading. Very “twiggy”. 45 feet tall by 40 feet spread.
Culture: Tolerates low moisture conditions once established. Adaptable to wind and alkalinity. Prone to snow load damage and decay.
Resources


