Ginkgo biloba (geenk’-go by-low’-bah)
Family: Ginkogaceae, Ginkgo
Key Steps
- 1b – Alternate leaf arrangement — go to 18
- 18a – Leaf simple — go to 19
Description
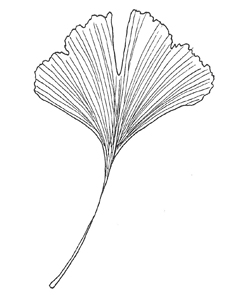 Leaf: Fan or triangular-shaped. Veins are parallel to side margins. Side margins are smooth. Top margin may have 2-3 lobes or a scalloped-appearing margin. Bright green.
Leaf: Fan or triangular-shaped. Veins are parallel to side margins. Side margins are smooth. Top margin may have 2-3 lobes or a scalloped-appearing margin. Bright green.
Bud: Brown, overlapping scales.
Stem: Thick, pale brown to gray. Stringy and peeling on older branches. Older branches have short, black spur shoots.
Bark: Ridges are gray-brown with dark, vertical furrows.
Flower: This tree is a member of the Gymnosperms, and therefore makes cones instead of flowers. Male cones are 1 inch long in early spring, green, on short shoots. Female cones are a long (up to 2 inches) stalk, greenish/white. Dioecious (separate male and female plants).
Fruit: Because this tree is a member of the Gymnosperms, it also does not make a true fruit. The female cone that bears the seeds is a fleshy, foul smelling cone approximately the size of a plum.
Habit: Slower grower. Starts out pyramidal then becomes open and broad. Large branching structure. 50 feet tall by 30 feet spread.
Culture: Full sun. Moderate moisture requirement. Adapted to sandy soil and pH levels. Protection from extreme wind. To avoid the smelly fruit, generally only males are planted.
Resources


