Ulmus pumila (Ul’-mus pu’-mi-la)
Family: Ulmaceae, Elm
Key Steps
- 1b – Alternate leaf arrangement — go to 18
- 18a – Leaf simple — go to 19
- 19b – Thornless — go to 22
- 22e – All leaves unlobed — go to 31
- 31d – Leaf is oval or oblong (twice as long as wide) — go to 40
- 40a – Leaf base asymmetrical — go to 41
- 41c – 1 main vein — go to 42
- 40a – Leaf base asymmetrical — go to 41
- 31d – Leaf is oval or oblong (twice as long as wide) — go to 40
- 22e – All leaves unlobed — go to 31
- 19b – Thornless — go to 22
- 18a – Leaf simple — go to 19
Description
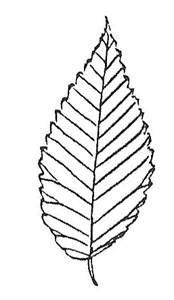 Leaf: To 3 inches long. Usually singly-toothed margin, pointed tip, may have a slightly uneven base. Pinnate venation. Leaf smaller and not as rough in texture as American Elm.
Leaf: To 3 inches long. Usually singly-toothed margin, pointed tip, may have a slightly uneven base. Pinnate venation. Leaf smaller and not as rough in texture as American Elm.
Bud: Roundish in shape. Flower buds are larger than the leaf buds, which are very thin and hard to see. Buds are reddish-brown or blackish and may be tipped to one side or the other of the leaf scar. Buds scales (4 or more) may be in 2 ranks (two vertical rows). Scales may be hairy on margins. True terminal bud absent.
Leaf Scar: Half round. Sunken bundle scars when visible are in groups of 3.
Stem: Slender. New growth gray, in a “fishbone” or herringbone pattern.
Bark: Older bark brown, furrowed.
Pith: White, solid.
 Fruit: Oval, circular, flat, papery, 1/2 inch diameter. In clusters of 8-15.
Fruit: Oval, circular, flat, papery, 1/2 inch diameter. In clusters of 8-15.
Habit: Scraggly, not vase-shaped. Weak wood, very fast growing. Prone to storm damage. 40 feet tall.
Culture: Thrives just about anywhere under any condition.
Note: Confused with Chinese Elm. Chinese Elm fruits in September, not in spring like Siberian Elm.
Resources


