Acer saccharinum (ay’-sir sak-ka-rie’-num)
Family: Sapindaceae, Soapberry
Key Steps
- 1a – Opposite leaf arrangement on stem — go to 2
- 2a – Leaf simple — go to 3
- 3a – Leaves are lobed — go to 4
- 4b – No milky sap — go to 5
- 3a – Leaves are lobed — go to 4
- 2a – Leaf simple — go to 3
Description
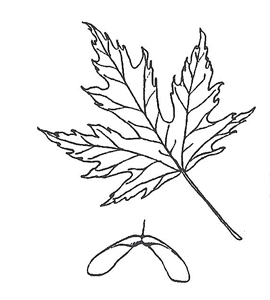 Leaf: Five pointed lobes; deep, U-shaped, toothless sinuses. Base of middle lobe is narrowed. Middle lobe may have 3 of its own smaller lobes. Medium green above, whitish beneath. Heart-shaped leaf base.
Leaf: Five pointed lobes; deep, U-shaped, toothless sinuses. Base of middle lobe is narrowed. Middle lobe may have 3 of its own smaller lobes. Medium green above, whitish beneath. Heart-shaped leaf base.
Bud: Reddish, blunt or slightly pointed, small. Scales overlap. Extra buds may be present above some leaf scars (there may be flower buds along with a leaf bud that is stalked.) Flower buds are fatter and may have hairy margins. Bud scales are sharper pointed at the tips on silver maple than they are on red maple. Terminal bud has 3-4 pair of scales.
Leaf Scar: Narrow, 3 bundle scars. Leaf scars are connected across the stem by a horizontal line.
Stem: Young stems are slender; reddish new growth, gray older growth of stems is smooth. Unpleasant odor when crushed.
Bark: Trunk bark on older trees is gray, shaggy and may peel off in vertical strips.
Pith: Solid, white.
Flower: Greenish-yellow to red, blooming before leaves appear (one of the first trees in our area to bloom). Short dense clusters. No petals.
Fruit: Double samara. Wings curving slightly at 90° angle.
Habit: Large shade tree. Spreading branches, narrow crotches, shallow root system. To 60+ feet tall. Fast growing, weak-wooded, susceptible to storm damage. Because of shallow roots will damage sidewalks and driveways.
Culture: Due to iron chlorosis (yellowing of leaves with veins remaining green) avoid planting in highly alkaline soils. Prefers high moisture conditions.
Resources


