Robinia pseudoacacia (Roe-bin-ee-a)
Family: Fabaceae, Pea
Key Steps
- 1b – Alternate leaf arrangement — go to 18
- 18b – Leaf compound — go to 58
- 58b – More than 3 leaflets — go to 59
- 59a – Entire or very finely serrate leaflet margins — go to 60
- 60a – Thorns — go to 61
- 61a – Pair of 1/4 to 1/2 inch prickles at nodes — Black Locust
- 60a – Thorns — go to 61
- 59a – Entire or very finely serrate leaflet margins — go to 60
- 58b – More than 3 leaflets — go to 59
- 18b – Leaf compound — go to 58
Description
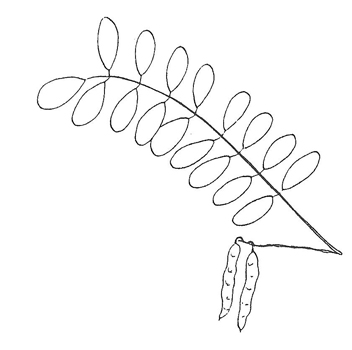 Leaf: Oddly pinnate, 7-19 leaflets, egg-shaped, each leaflet 1 -2 inches long, smooth margins. Each leaf 6-14 inches long. Center vein is flat on upper surface, grooved and rounded beneath. Older foliage dark blue-green, new foliage bright yellow-green.
Leaf: Oddly pinnate, 7-19 leaflets, egg-shaped, each leaflet 1 -2 inches long, smooth margins. Each leaf 6-14 inches long. Center vein is flat on upper surface, grooved and rounded beneath. Older foliage dark blue-green, new foliage bright yellow-green.
Bud: Tiny, may be completely submerged into stem. Rusty-colored hairs. 3-4 buds clustered, covered with overlapping scales. True terminal bud absent. Scales are brown outside, woolly inside.
Leaf Scar: Nearly circular. 3 bundle scars.
Stem: Hairless, reddish-brown, brittle, zig-zaggy. Ridges along stem from leaf scars. Pair of thorns at leaf axils.
Bark: Heavy, disorganized ridges.
Pith: Brown, solid.
Flower: Creamy white, fragrant clusters, 4-8 inches long. Pea-like blossoms, usually in clusters.
Fruit: 2-6 inch flat pods, thin, papery, reddish-brown, smooth. Persist through winter.
Habit: Irregular branching. Suckers. Can form a thicket.
Culture: Very adaptable.
Note: Young leaves, seeds, roots, and inner bark are poisonous.
Rose Locust (Robinia neomexicana) — Similar to Black Locust except flowers are lavender-rose and the fruit pods are smaller and have glandular hairs. Hairy flower stalks and hairy buds. Glandular, rusty hairs on stems. Naturalized.
Idaho Locust (Robinia. ‘Idaho’) — Lavender-rose flowers. More of a single-trunked tree form. Cultivated.
Resources




